The success of platforms like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Glovo has set a high bar for convenient ordering and continues to fuel a growing global demand for food delivery applications. According to Statista, the number of users in the Meal Delivery market is expected to reach 2,5 billion users by 2030. Businesses ranging from local restaurants to major food service brands and grocery chains are exploring how to enter this expanding digital ecosystem. The pertinent question: development cost of a food delivery app.
The price of mobile app development depends on various factors, including the chosen platform, required features, technology stack, and regional development rates. Not to mention the hidden costs that you may face in the process. Understanding these factors will help you estimate the budget and avoid overspending. In our article, we will discuss the average app prices and break down the food delivery app development cost.

How much does it cost to build a food delivery app?
To give you a general idea, the average cost of a custom food delivery app development can range from $20,000 to $300,000+. The price typically falls into one of the three categories:
- Basic food delivery app: $20,000–$40,000. Usually, an MVP of a single restaurant or a simple startup. Basic apps include essential features for customers to browse menus, order food, and pay online, and for restaurants to receive those orders.
- Mid-range application: $40,000–$100,000. It can be an aggregation platform for more than one restaurant. The features include everything in basic plus real-time order tracking, user reviews, promo codes, and a simple admin panel.
- Advanced app: $80,000–$250,000+. The type of platforms like Uber Eats or DoorDash that include everything from the mid-range level, plus a dedicated app for delivery drivers, intelligent features like personalized recommendations, and advanced business analytics.
Mind that all the prices we provide in our article are approximate, and the final development cost will depend on your business needs and other factors that we’ll discuss further.
Key factors influencing food delivery app development cost
As we mentioned, developing a food delivery app involves multiple technical and business decisions that affect the overall application cost. Here are some of the main factors that you need to consider during the budget planning.
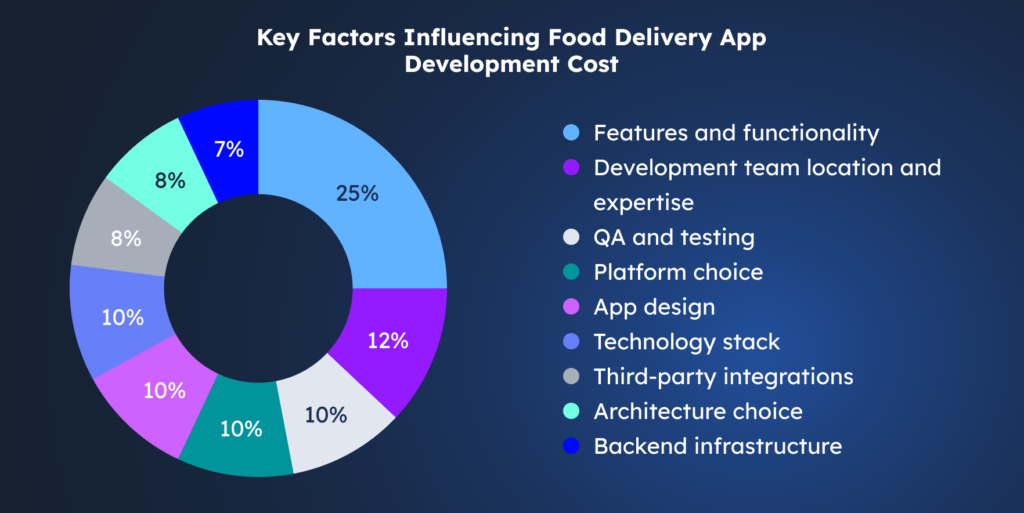
Features and functionality
This is the biggest cost driver. That’s because each feature directly translates into development hours, technical complexity, and ongoing maintenance. Naturally, the food delivery app with basic features (menu, cart, payment) costs less. Advanced features like real-time GPS tracking, AI recommendations, in-app chat, and loyalty programs will add to the overall price.
Development team location and expertise
The cost of developers varies dramatically by region. Hiring a team in North America or Western Europe would be more expensive, agencies in Eastern Europe or Asia offer more competitive rates. Furthermore, a team with specific expertise in marketplace apps may have a higher rate but will work more efficiently, often providing better long-term value.
QA and testing
There’s no mobile app development without quality assurance and testing. For a food delivery app, this means making sure payments never fail, orders always go to the correct restaurant and customer, and the live delivery tracker updates smoothly. QA engineers test the app on many different phones and operating systems to ensure it works for everyone. This process is crucial because a single bad experience can cause a user to delete your app and never return. For a comprehensive testing process on a mid-level app, you should budget approximately $8,000 to $25,000.
Platform choice
When building a mobile app, targeting both iOS and Android users is essential to reach the broadest possible audience. Therefore, you have two options here: develop two separate native applications, or one cross-platform app.
Performance-wise, the native development will give you full access to all device-specific features and a smoother user experience, but increases the initial build cost. On the other hand, cross-platform development is generally faster and more cost-efficient, making it a popular choice for startups and businesses with limited budgets.
App design
Thought out user experience translates to higher retention rate, repeat purchases and higher transaction value. But poor design can frustrate users and lead them to abandon the app, regardless of its features. Therefore, it’s important to plan an intuitive user journey that makes ordering food effortless. A simple yet functional design with basic features can cost around $5,000–$50,000. A high-quality, custom design can help to build a strong brand identity, but requires significant investment, as the price can range anywhere from $50,000 to $130,000.
Technology stack
This is a foundational decision that impacts the app’s performance, scalability, and long-term maintenance. Selecting modern, well-supported, and scalable technologies ensures that the app can handle growth and is easier to update. On the contrary, choosing outdated or obscure technologies can lead to higher development costs due to a smaller pool of available talent, greater difficulty in finding solutions to problems, quickly accumulating technical debt and potential performance bottlenecks down the line. In the worst case scenario, an app built with an outdated tech stack will need to be rebuilt incurring much greater costs.
Third-party integrations
Integrations with external services are essential for core functionality, but they add complexity to both the development phase and long-term maintenance. The cost increase comes from the significant development time required to study API documentation, write robust connection code, handle errors, and ensure reliability through rigorous testing.
Common integrations include:
- Payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal);
- Maps and geolocation APIs (Google Maps);
- SMS and notification services (Twilio, Firebase Cloud Messaging);
- Analytics tools (Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Firebase);
- Authentication and security services (Auth0, Firebase Authentication).
It’s important to note that some services, like authentication, are designed to help save on the cost of building complex systems from scratch. However, all integrations carry potential setup efforts and ongoing usage charges. For example, payment processors like Stripe or PayPal take 2,9% + fixed fee per transaction, while SMS services may charge per message sent. So that’s also something you need to consider while planning your project budget.
Architecture choice
The app’s architecture defines how its components interact. A monolithic architecture is quicker and cheaper to develop, making it suitable for MVPs or small-scale products. On the other hand, a microservices architecture provides better scalability and reliability but increases complexity and initial costs due to the need for separate modules, databases, and deployment pipelines.
Backend infrastructure
This is the engine that powers your app, handling users, orders, and data. A simple setup for a small user base is affordable. However, a robust, scalable cloud infrastructure (like AWS or Google Cloud) designed to handle thousands of simultaneous orders requires more initial development and incurs ongoing, usage-based server costs.
Food delivery app development budget planning: detailed cost breakdown
Now that we have discussed the factors that influence the cost to develop a food delivery app, it is time for a detailed budget breakdown. The total investment can be segmented into:
Application type and complexity
Food delivery solutions consist of several interconnected modules, and each module impacts your budget differently. The more user roles, features, and customization you introduce, the higher the cost and delivery time. Typically, a complete ecosystem includes:
- Customer app, which users download to browse restaurants, order food, and track your delivery.
- Courier app that allows the delivery drivers to receive orders, navigate to the restaurant and customers, and confirm deliveries.
- Vendor portal (optional) used by the restaurants to manage incoming orders, update their menu, and track their sales.
- Admin panel for a company to manage the entire platform operations in one place.
Each of these components has its own development scope, data flows, and user logic, so they need to be built and tested individually. Here’s the approximate development costs table.
| Component | Key features | Estimated development cost |
|---|---|---|
| Customer app | User registration, restaurant search, menu browsing, cart and checkout, multiple payment methods, order status tracking, reviews and ratings, push notifications, loyalty features. | $25,000–$70,000 |
| Courier panel | Registration and verification, order acceptance, delivery status updates, route navigation, availability toggle, delivery history, in-app communication. | $20,000–$70,000 |
| Vendor panel | Menu and pricing management, incoming order management, order status updates, schedule management, inventory, analytics, promotions, branch-level control. | $20,000–$50,000 |
| Admin panel | User and restaurant management, order and delivery monitoring, financial reporting, refunds, promotional tools, multi-role permissions, analytics dashboards, platform settings. | $10,000–$50,000 |
There are also different types of food delivery applications that serve different audiences and operational models. These are:
- Restaurant aggregators. A marketplace connecting many restaurants to customers (like UberEats or DoorDash). Requires building and synchronizing four separate applications (Customer, Courier, Restaurant, Admin), leading to a development price typically between $30,000 and $250,000+.
- Restaurant-to-consumer delivery apps. Applications for a single restaurant or chain (like Domino’s or McDonald’s). Focuses on a high-quality Customer App and a simple Restaurant Panel, with costs ranging from $40,000 to $100,000.
- Grocery delivery. On-demand delivery from grocery stores and food warehouses. This is one of the most complex models because it requires building and synchronizing three core components: a real-time inventory system, a vast product catalog, and a dedicated shopper app for order fulfillment. Therefore, the development costs can range from $150,000 to $400,000+.
- B2B food delivery. Catering and meal delivery for offices and businesses. The complexity lies in features like corporate accounts, bulk ordering, and sophisticated invoicing, with development costs between $100,000 and $250,000+.
The development price for each application depends on its complexity and development time.
| The level of complexity | Development time | Approximate cost |
|---|---|---|
| Basic app\ MVP | 2–4 months | $20,000–$40,000 |
| Mid-range app | 3–6 months | $40,000–$100,000 |
| Advanced app | 6–12 months | $80,000–$250,000+ |
Development team region
The region you choose to hire developers from will strongly influence your final budget as well. Rates vary based on local living costs, demand, and developer experience. Here are the approximate prices for mobile app development based on the team’s location.
| Region | Development rate (per hour) |
|---|---|
| North America | $100–$180 |
| Western Europe | $90–$140 |
| Eastern Europe | $40–$70 |
| Latin America | $30–$70 |
| South Asia | $25–$50 |
Calculate team cost for your food delivery app development
Hidden costs to consider during budget planning
When planning your budget, don’t just calculate the cost of building the app. Be sure to include the ongoing expenses that are necessary for long-term operation. These are:
- Maintenance and updates. After launch, your app will require regular updates, performance improvements, and bug fixes to remain stable and competitive. Maintenance typically costs 15–25% of the initial development cost per year and ensures compatibility with new system versions and devices.
- Marketing and promotion. Building the app is only part of the process. To attract users, you need an effective marketing strategy. App store optimization, social media advertising, and influencer collaborations can be quite costly starting from the launch phase and can continue to add up through monthly expenses for retention campaigns.
- Legalization and compliance. Ensuring compliance with data protection laws (like GDPR or CCPA), acquiring necessary business licenses, and drafting partnership or service agreements all involve legal fees. These costs can vary depending on the markets you operate in and the complexity of your business model.
- Customer support. Providing reliable support enhances user satisfaction and retention but adds ongoing costs regardless of the approach (chatbots, email support, or a 24/7 helpdesk) you choose.
- App store fees. If you want to publish your app on the store platforms, you will need to have a developer account. The Apple App Store charges an annual membership fee of $99 a year for individual profiles and $299 a year for organization accounts. Google Play charges a one-time registration fee of $25, after which you can publish unlimited apps without additional fees. Additionally, both platforms take a 15–30% commission from each in-app purchase or transaction.
6 smart ways to optimize your development budget
1. Start with a minimum viable product
Instead of building a full-featured app from day one, launch with only the core features that solve your customers’ main problem (e.g., browsing a menu, ordering, and paying). This approach will let you test your business idea with real users for a much lower initial investment. You can then use their feedback to guide future development, ensuring you only spend money on features that users actually want.
2. Consider coss-platform development
Opting for cross-platform development allows you to write one codebase that works on both major mobile platforms. This strategy significantly cuts development time and cost compared to building two native apps, making it a smart choice for startups and businesses focused on efficient budgeting.
3. Hire an experienced development team
While a lower hourly rate might seem attractive, a team with a proven track record in building marketplace apps will work more efficiently and make fewer costly mistakes. Their expertise helps avoid common architectural errors and ensures the app is built on a scalable foundation from the start. This saves money on extensive reworks and fixes down the line, making it a cost-effective choice in the long run.
4. Use open-source tools
Using robust, open-source tools and frameworks for your backend, database, and other components can drastically reduce costs. These tools are free to use and supported by large communities, which means you avoid expensive licensing fees for commercial software and have access to a wealth of shared knowledge and solutions.
5. Set clear feature scope
Define a clear, prioritized list of features for your initial launch and stick to it. Continuously adding something new during development is a major budget killer. When we work on a project, fixed scope plus rigorous effort estimation for each development stage is our best practice to avoid unplanned expenses.
6. Reuse UI components and templates
Instead of designing and coding every button, menu, and screen from scratch, leverage pre-built UI kits and templates for your chosen framework. It will save both design and development time, which your team can spend on building custom parts of your app.
Conclusion
Developing a food delivery app involves a range of factors that collectively determine its cost, from feature complexity and design to regional labor rates and ongoing maintenance. While prices vary widely, most businesses can expect to invest between $20,000 and $250,000 for a fully functional product, with additional expenses for updates and marketing.
If you’re ready to take your business to the next level with a custom, user-friendly food delivery application, you can rely on SoftTeco as your trusted technical partner. With extensive experience in creating mobile and web applications, we guide our clients through the entire process from the initial idea to launch and further partnership. Feel free to contact us for a consultation.


Comments