Artificial Intelligence has become a widely used technology across many industries, and manufacturing is no exception. Nowadays, manufacturing companies face a number of challenges, such as equipment downtime, low process efficiency, and increased costs. Most of these problems can be solved with AI. This is why it is being actively implemented in manufacturing.
So how exactly does AI in manufacturing help business owners gain a competitive advantage and improve their processes? This article aims to answer these questions and discuss the core applications of AI in manufacturing, its benefits, real-world examples, and the future outlook.

AI in manufacturing explained
AI in manufacturing implies the use of artificial intelligence technology, including robotic process automation, computer vision, machine learning, to optimize and automate common manufacturing processes. Its use helps resolve the biggest manufacturing challenges, like poor inventory management or labor shortages, and reduce operating costs through smarter, data-based strategic planning.
Numerous reports confirm the rising popularity of AI in manufacturing sector:
- Currently, 60% of companies use AI in manufacturing in 2026; this number is expected to reach 80% by 2030.
- The global AI in manufacturing market is projected to see $155.04 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 35.3%.
These reports and many like them make it safe to assume that AI development will only become more prevalent across industries and more business owners will invest in this technology.
AI use cases in manufacturing
Since the manufacturing industry is the cradle of modern process automation, it is a great field for integrating AI as it can be applied to virtually any parts of the manufacturing process. Below, we will discuss the most prominent AI applications in manufacturing.
Digital twin
Manufacturers now use digital twin technology or a virtual copy of production processes at the smart factory. Combined with machine learning, it significantly improves production efficiency. Manufacturers can simulate, monitor, and optimize operations without affecting the physical asset. A digital model is regularly updated with live data from IoT sensors, analyzed through deep learning and ML algorithms, to maintain an accurate virtual representation.
By modulating production processes in a digital twin, manufacturers can identify and resolve process bottlenecks or equipment issues early. This helps them optimize equipment performance through predictive maintenance. Also, it allows them to do virtual prototyping and testing of the new product, and, as a result, eliminate many physical iterations. By continuously monitoring quality parameters, a digital twin can help reduce product defects and rework. Thus, according to the Infotech research, this technology helps increase production volumes and reduce new-product time-to-market by 20–50%.
For example, the BMW Group implemented its “Virtual Factory” to create digital replicas of more than 30 production sites to accelerate global production planning. The virtual factory includes equipment data, logistics data, vehicle data, and even a 3D simulation of manual work processes. Using NVIDIA Omniverse, the company can run real-time simulations in 3D to test and optimize factory systems virtually before implementing changes in the real world.
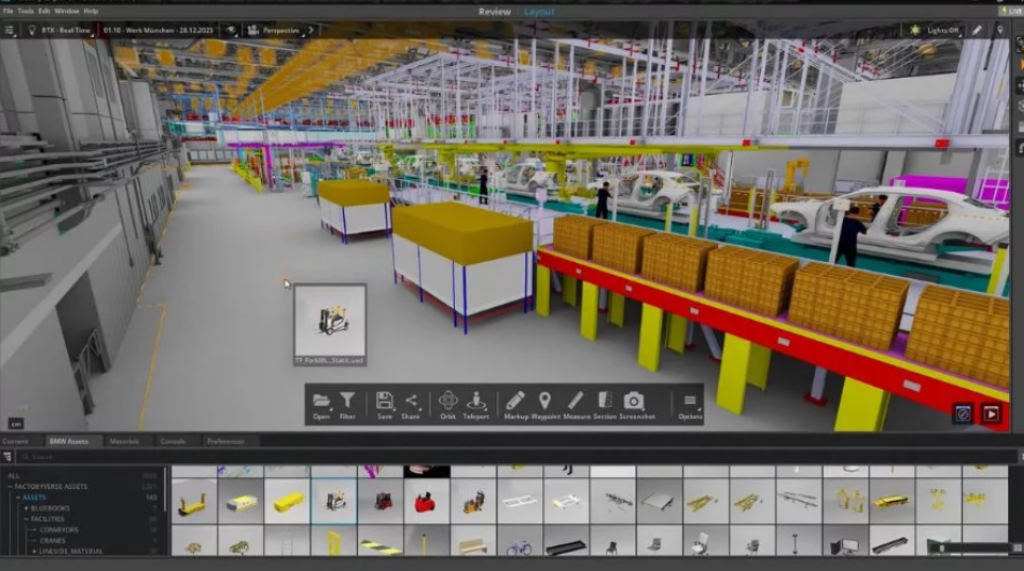
BMW Group virtual factory. Source: BMW Group
Quality control automation
With the help of computer vision and machine learning, the product quality process can be almost completely automated. AI models analyze product images, instantly spot defects or damage, and notify employees in real time. They can do it with greater accuracy than human inspectors. These checks enable companies to reduce downtime associated with quality control by 30%, reduce the risk of human error and deliver high-quality products to end users.
Predictive maintenance
Since the maintenance and repair costs are always high, it is more beneficial for companies to reduce them through proactive and timely maintenance. Artificial intelligence can help detect any issues or defects at early stages and prevent system breakdowns before they happen through computer vision and real-time data processing. Predictive maintenance can help manufacturing companies reduce costs by up to 40%, reduce equipment downtime by 50%, and extend machine life by 20%.
Another way AI helps with predictive maintenance is through a digital twin, creating a real-time digital replica of a physical facility. Companies can interact with digital twins, apply various scenarios to them, and analyze how a facility would behave in different situations. Digital twins can also highlight existing or potential problems within a facility and suggest ways of workflow optimization.
Collaborative robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are a new generation of industrial robots explicitly designed to work alongside people in a shared workspace. They usually have rounded edges, low weight, and are designed with safety first. Also, they feature sensors to avoid collisions with people, are flexible, and require a lower initial investment compared to traditional industrial robots. Examples of tasks performed by cobots in the production environment are:
- Welding and gluing product parts
- Picking and packaging products
- Material transport
- Quality control
Most of these tasks are repetitive and simple and often do not require human assistance or control. Given that most industrial cobots are affordable, their deployment can significantly increase operational efficiency and free employees from mundane tasks that consume too much time. For example, automakers BMW uses collaborative robots on assembly lines at its Spartanburg manufacturing plant. Collaborative robots equip the insides of the doors of BMW models with sound and moisture insulation. This protects electronics in the door and the entire interior of the car from moisture.
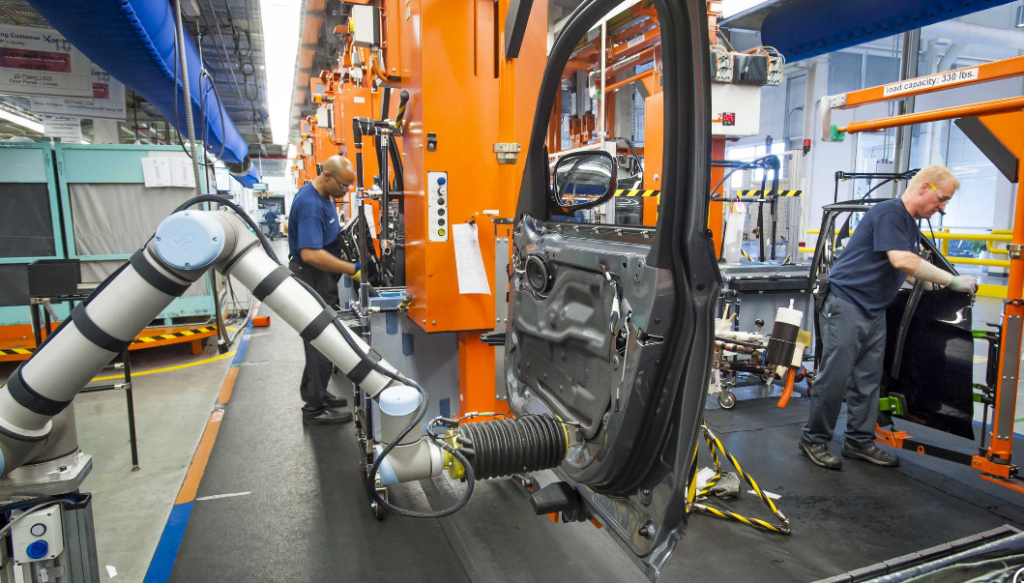

Collaborative robot at BMW’s Spartanburg manufacturing plant. Source: BMW Group
Order management
AI systems can automatically check, confirm, and process orders, reducing manual labor and errors. Beyond this, AI improves order management through:
- Smart analysis of customers’ preferences
- Smart inventory management
- Detection of fraudulent activity
- Dynamic pricing changes
AI streamlines communication across the entire fulfillment chain, ensuring that suppliers, warehouses, and delivery teams stay aligned in real time. As a result, AI helps make the order management process more data-driven and user-centric while also eliminating the biggest bottlenecks that are common for the process.
Product development and design
Companies can use AI to streamline product development in several ways. First, AI-powered platforms can assist in data collection and analysis, such as current trends, user demographics, competitor analysis, etc. Second, employees can use these reports to come up with an idea of a competitive and user-centric product. This way, AI greatly saves time and effort on data research and analysis. As a result, companies can accelerate product development cycles and bring truly innovative products to market.
For example, a company plans to launch a new line of industrial equipment. They use an AI-powered analytics platform to scan data from sensors on existing equipment, failure and maintenance reports, and customer requests. Based on this collected data, the team can develop a product concept aligned with real production needs rather than at random. For example, it might be equipment with automatic temperature control or AI-based predictive maintenance.
Supply chain management
Supply chain management is an essential part of any manufacturing business and includes several stages, like production planning, sourcing, logistics and more. AI in the manufacturing industry helps streamline and organize almost all processes and adds transparency to the whole supply chain in the following ways:
- ML-based demand forecasting and more accurate stocking
- Logistics optimization through smart route planning
- Inventory automation and optimization
- Automation of warehouse operations
- Smart quality checks and instant defect detection
And obviously, these are not all examples. AI makes supply chain management more autonomous, transparent, and organized, enabling business owners to instantly access any needed information and seamlessly share it across departments. For example, Amazon uses AI systems to predict daily product demand and determine where to source orders based on its historical data. In other cases, AI is used to optimize warehouse restocking and improve how goods are stored and moved.
Energy management
AI-based energy management tools analyze data from equipment, sensors, and production lines in real-time. ML models can identify when energy consumption exceeds the norm, such as during idle time or peak loads. Then, they recommend specific actions, such as adjusting equipment settings or turning off non-critical equipment. These actions can be automated by integrating AI with energy management systems (EMS) or manufacturing execution systems (MES). It helps manufacturing companies to use energy sparingly and achieve significant cost savings.
Contract management
Supplier contract management is a complex yet vital process in manufacturing that is related to numerous stakeholders and legal documents. Such contracts typically include key financial details, such as delivery terms, payment deadlines, penalties for delays, and more. They require careful analysis, which is often time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Technologies based on artificial intelligence and natural language processing have significantly simplified this process. Instead of lawyers and managers manually viewing hundreds of pages, NLP algorithms can automatically extract key data from contracts for analysis. AI systems can significantly increase document processing speed and reduce the number of human errors that can occur during manual processing.
Workforce management
Artificial intelligence assists in workforce planning and management. ML models can analyze historical data on employee workload, skills, and productivity to optimize work schedules. This helps manufacturing companies minimize downtime, avoid labor shortages, and reduce overtime costs.
In addition, AI is used to monitor employee productivity. By collecting data on work speed, task accuracy, and the time required to complete various tasks, ML can identify weaknesses and offer personalized recommendations or additional training. Also, AI can be used to identify potential safety hazards at a factory by analyzing video surveillance, sensors, and equipment data. Thus, AI contributes to improving employees’ working conditions and helps reduce the number of accidents and injuries.
Document search and analysis
Manufacturing companies often deal with different documents, including technical records, instructions, and equipment repair histories. These documents come in a variety of formats, such as text, graphics, and tables. Generative AI enables efficient processing and extraction of critical information from all these sources. It can automatically summarize the contents of long and often complex documents without having to read everything from beginning to end.
Instead of manually searching through all of the documents, users can ask the AI a specific query. By analyzing the query context, AI can provide users with the most necessary information.
The benefits of AI in manufacturing
AI won’t bring much benefit if it was not implemented for a specific goal. Instead, it can become a sunk cost and derail existing processes. This is why it is important to understand how exactly AI can help your business and what benefits you can expect from its deployment.
Increased efficiency
Artificial intelligence systems can automate many routine and repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on more complex and valuable tasks. By automating mundane processes and making data-driven decisions, manufacturers can greatly reduce downtime and empower their employees. This increases productivity and production efficiency.
Better quality
Automation of quality control significantly minimizes a chance of defects in a production line. Ultimately, it improves the quality of manufactured goods. AI can help manufacturers find and correct potential issues before they become larger problems. Also, automated quality control results in improved customer satisfaction and a reduced number of returned products.
Enhanced security and safety
AI can greatly assist in maintaining sufficient safety levels in the manufacturing environment. Smart AI solutions and computer vision are used for real-time monitoring of the production environment, employee health monitoring, or the automation of hazardous tasks. The result is precise task completion and reduction in the overall number of accidents.
Informed decision-making
Artificial intelligence processes data in real time, allowing production managers to make business decisions based on accurate data. Using a digital twin also helps improve decision-making by enabling the modeling of production scenarios and testing before full-scale implementation. It reduces the likelihood of errors and allows manufacturers to make smarter decisions.
Cost reduction
Artificial intelligence analyzes production data in real time, identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource allocation. It helps companies reduce costs and operate more efficiently. Predictive analytics allows companies to anticipate maintenance needs and thereby reduce costly downtime and energy consumption, leading to lower expenses.
Asset reliability
Artificial intelligence improves asset reliability through predictive maintenance. ML models analyze sensor data to predict failures and plan repairs in advance. By doing this, companies can extend equipment lifespan and reduce the number of faulty machines.
Sustainability
AI solutions help use resources more efficiently, reduce energy consumption, and make production more environmentally friendly. Also, innovative AI systems monitor equipment condition, reducing maintenance requirements.
Competitive advantage
AI helps manufacturers optimize production and reduce downtime through predictive analytics, as well as improve product quality through real-time quality monitoring and computer vision. The results are reduced product time-to-market and better design quality, which allows companies to adapt to market changes more quickly while remaining competitive.
The main challenges of AI in manufacturing
As well as manufacturing software development, AI design comes with a certain set of challenges that stop companies from AI implementation. Here are the main ones.
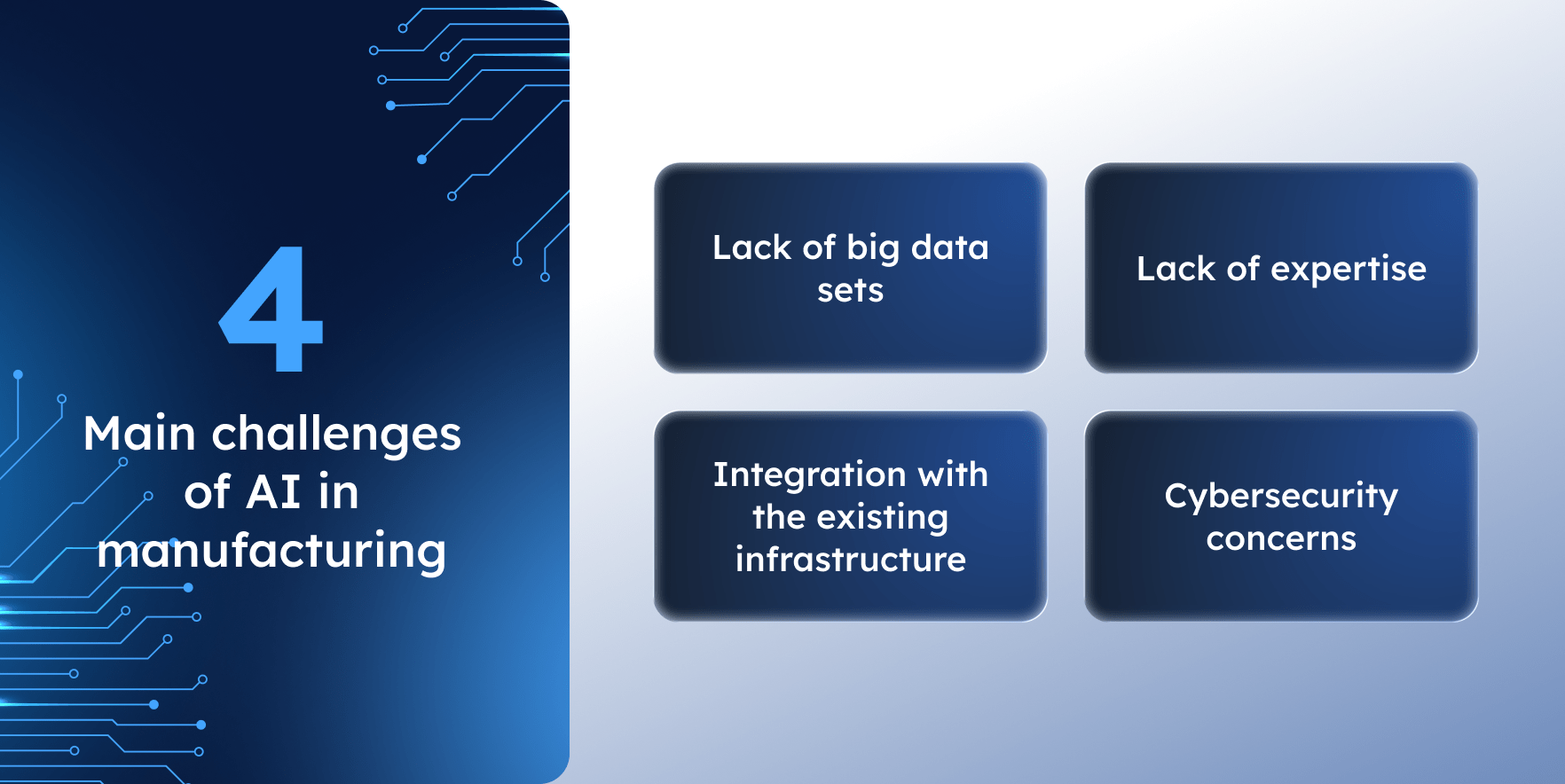
Lack of big data sets
To obtain accurate results, AI models need to be trained on large datasets. Therefore, if your company doesn’t have this data, AI won’t deliver the expected results and a meaningful return on investment.
To avoid this problem, you need to prepare large datasets and ensure they are in a suitable format. On top of that, the data pools must be maintained and updated continuously so the data fed to the AI remains relevant. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is to use a MES (manufacturing execution system) that automatically collects and sorts data from multiple sources.
Lack of expertise
To properly deploy and maintain an AI model, manufacturing companies need skilled specialists with a deep understanding of data analysis and AI. The company may not have such specialists among its in-house employees. Lack of needed expertise hinders the use of AI, reducing model accuracy and increasing the risks of errors.
To overcome this issue, companies should hire short-term experts for a particular AI project. They can consult with an IT provider to select a team of necessary specialists, including data engineers, data scientists, ML engineers, data analytics leads, etc. They can also invest in training and reskilling in-house workers to improve their AI knowledge.
Integration with the existing infrastructure
Manufacturing facilities may have legacy software that hasn’t been optimized in a long time. In this case, when integrating AI with existing systems and processes, technical problems may arise due to incompatibility, outdated data formats, and limited resources in legacy systems.
If your software is outdated and can’t support AI implementation, you will have to update and optimize it. Some business owners may not be ready to face additional costs. But it is necessary to ensure smooth AI integration and work in the future. It’s recommended to build data pipelines and middleware to enable seamless communication between legacy systems and AI models.
Cybersecurity concerns
AI systems in manufacturing rely on a range of IoT sensors, devices, and cloud platforms. This creates a large digital attack surface. In other words, the more connection points a system has, the more likely hackers are to find a way in.
To ensure AI system security, implement comprehensive security measures, including data encryption, multi-factor authentication, strong access controls, and network segmentation. You should also regularly update and patch systems, monitor network activity, and carry out security audits and penetration testing. It’s recommended to train staff on cybersecurity best practices to improve their awareness and knowledge.
Real-life examples of AI in manufacturing
Many well-known companies, that have implemented AI into their business processes, are already taking full advantage of the numerous benefits of this technology.
General Motors
General Motors (GM), an American multinational automotive manufacturer, uses AI to improve vehicle production. By utilizing ML algorithms, GM analyzes data from sensors installed on assembly lines. This analysis allows the company to predict equipment failures with high accuracy, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. AI and machine learning enable the company to quickly and accurately pinpoint potential leaks in battery packs. It allows for quick repairs and supports the safety and quality of batteries.
Also, AI systems, combined with computer vision technology, detect imperfections and deviations from quality standards in real time. This ensures that only vehicles that meet GM’s strict quality criteria leave the factory. Apart from that, GM uses AI to deliver an exceptional driving experience. Using data such as customer interactions, sales, and manufacturing metrics, AI solutions provide insights into how to adjust production to ensure vehicles offer the features customers want most.
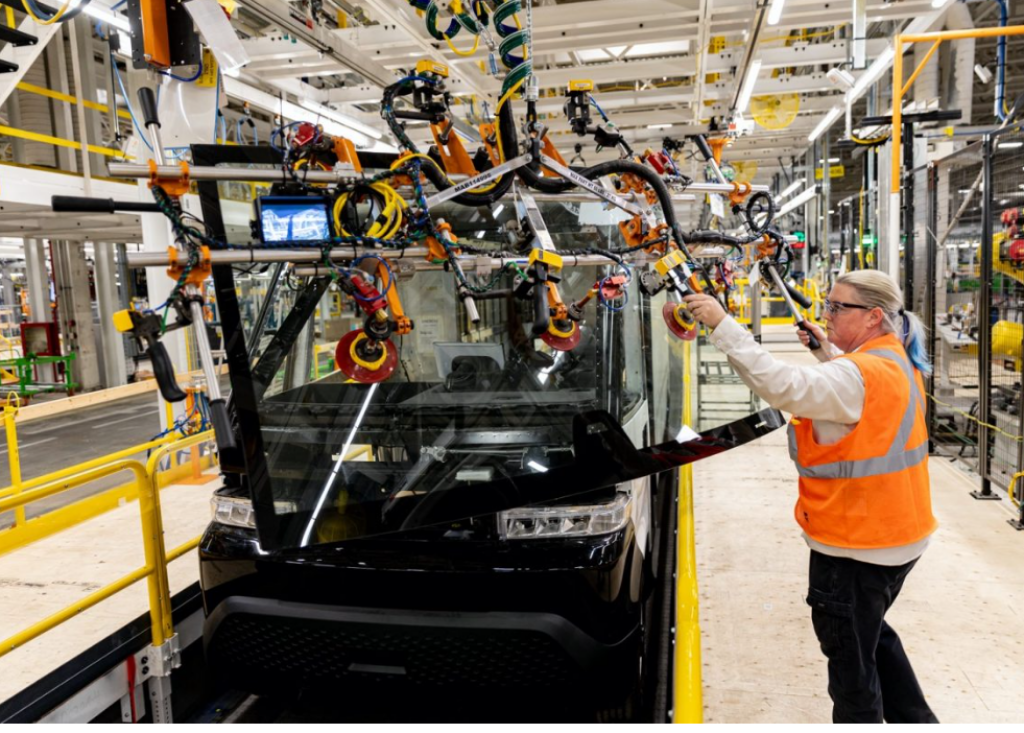

General Motors uses AI for vehicle production. Source: GM Authority
Siemens
Siemens, a German technology company operating across many sectors, uses AI to improve predictive maintenance, worker safety, and productivity. The company introduced one of its products, Senseye Predictive Maintenance. It provides insights into how well machinery, tools, and other factory infrastructure are operating and helps predict maintenance issues. The company reports that firms using Senseye Predictive Maintenance can cut maintenance costs by 40%, boost productivity by 55%, and reduce downtime by 50%.
With Microsoft, the company introduced Industrial Copilot, a generative AI assistant for engineers in industrial settings. It can quickly identify problems and provide advice to support engineering tasks, such as troubleshooting and equipment maintenance. When the tool identifies a problem, employees can use voice commands in any language to create a work request, which is instantly sent to the global team. The company reports the tool can improve “human-machine collaboration” and help address labor shortages.
The company also released Inspekto, an AI-based visual quality inspection system, that enables manufacturers to automate defect detection in their production lines. Using computer vision and machine learning, the system can detect anomalies or defects in the surface of parts and products in real time. It reduces reliance on manual inspection, improves product quality, and reduces rework, defects, and warranty costs.
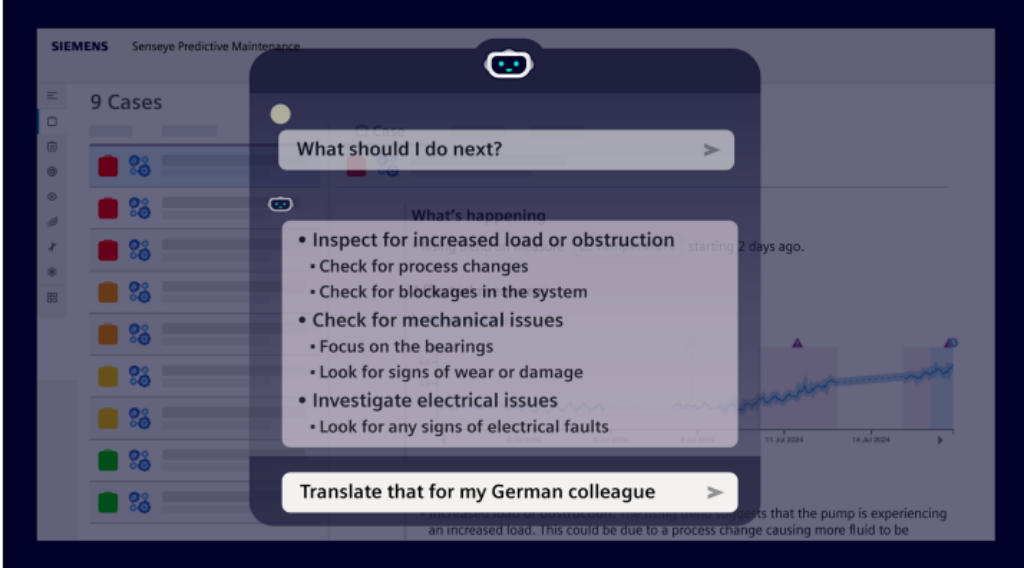
Senseye Predictive Maintenance tool. Source: Siemens
ZF Group
ZF Group, a German manufacturer of mechanical components for the automotive industry, uses AI to improve its development process. First, AI is used to analyze client requirements early in the project process. It identifies recurring patterns and suggests ready-made solutions based on past developments. It accelerates knowledge sharing between teams and improves the accuracy of design and engineering decisions. Second, generative AI is used to automatically generate requirements, drawings, mockups, and code for components and systems of automotive solutions.
Third, AI assists in the validation process. It replaces traditional, hardware-intensive testing methods with data-driven simulations and predictive models. These methods allow for faster testing of solutions and reduce development time. It also helps coordinate the processes of development and testing of сomponent, thereby reducing equipment and resource costs.
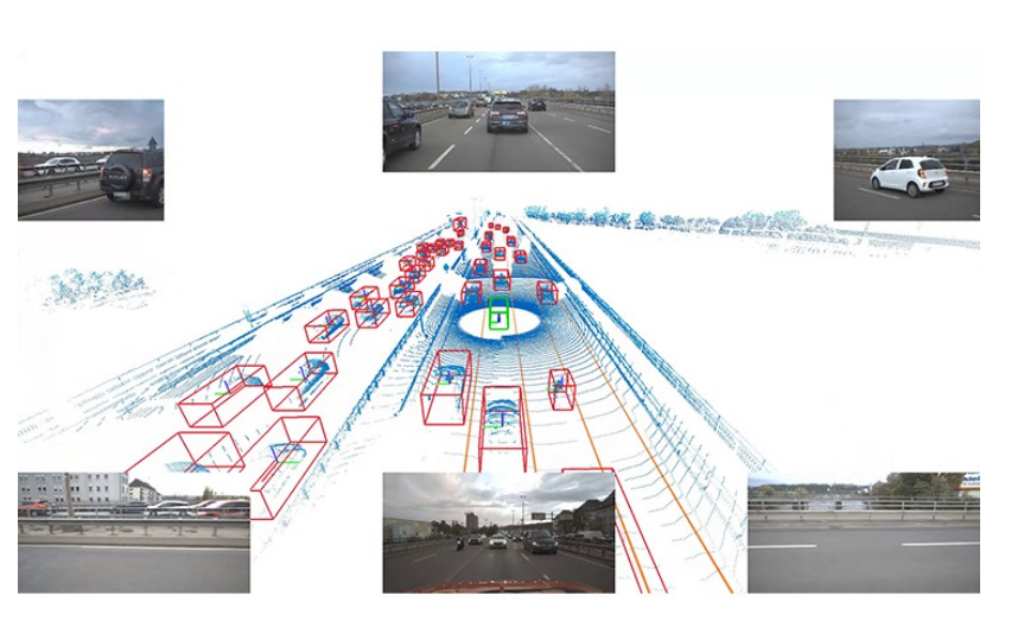
AI-supported validation solution for testing and training modern ADAS/AD systems. Source: ZF Group
BMW Group
BMW Group, a German multinational manufacturer of luxury assets, uses AI to make vehicle construction faster and more reliable. It leverages its own products, such as Car2X and AIQX. Car2X is a cloud-based platform enabling real-time communication and interaction between the vehicle and the BMW production system. The platform allows vehicles to self-analyze assembly status, detect errors with built-in cameras, and communicate real-time data to workers and systems. The AIQX IT platform uses sensor technology and AI to automate quality control processes. ML algorithms analyze real-time data and immediately send feedback to production line workers via devices.
Also, the company uses acoustic analytics. This is an AI model that automatically checks audio quality. All driving noise is recorded by microphones in the car seats, which are analysed and classified by AI. This is the final check before the vehicle is handed over to the customer.
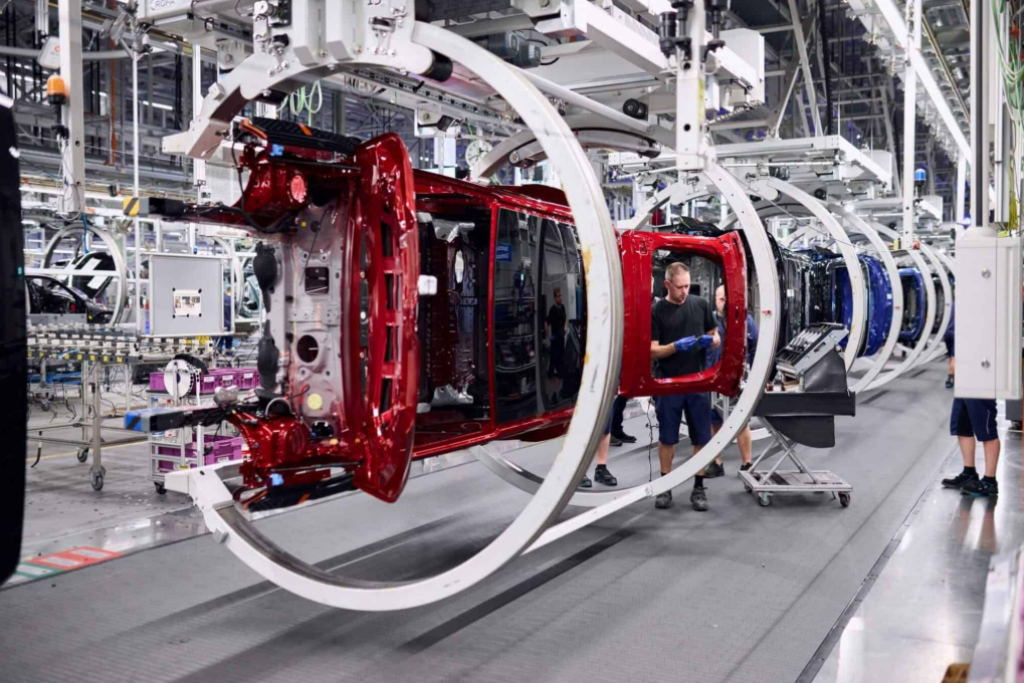

The AI system monitors assembly line conveyors at BMW’s factory in Regensburg, Germany. Source: BMW Group
The future of AI in manufacturing: trends
The application of artificial intelligence in manufacturing is constantly evolving, with new advances emerging regularly. Here are some key trends to watch out for in the year 2026 and beyond.
Generative AI
Engineers and designers use generative AI to generate multiple design variations and explore creative concepts. For example, in automotive and aerospace, engineers can use generative AI tools to design lightweight, efficient components. With it, manufacturers can evaluate multiple design options faster and accelerate the development process. Although this technology has already proven itself, its full potential is still being explored within the next few years.
Virtual and augmented reality
First of all, VR and AR technologies are being used in manufacturing for employee training. Virtual reality creates a fully simulated environment where workers can safely practice operating equipment or responding to emergencies. AI makes VR training smarter. It adapts scenarios to employee actions, simulates real-world or emergency situations, and analyzes training effectiveness. It reduces the need for expensive physical training and allows for safe training on complex or hazardous equipment.
Second, augmented reality allows engineers and designers to visualize 3D models of products or equipment to see how they fit into real space. Artificial intelligence allows manufacturers to instantly analyze 3D models, identifying potential design issues or suggesting improvements. This way, teams can move around the model, inspect it, identify and resolve design flaws early on.
Third, VR and AR are also used for real-time production monitoring. For example, AR devices such as smart glasses overlay real-time production data onto actual equipment. Workers can see metrics such as equipment temperature or maintenance alerts. AI further enhances this by processing real-time data to predict equipment failures, make corrections faster and increase the overall efficiency of the production line. As these technologies develop, they will increasingly and more deeply infiltrate production processes.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology is used alongside AI to improve transparency and traceability in supply chains. Blockchain stores all data in such a way that it cannot be altered or deleted. Meanwhile, AI can analyze blockchain data to predict supply chain disruptions, optimize delivery routes, and identify bottlenecks in production. In quality control, AI can automatically flag anomalies in production data recorded on the blockchain to ensure better adherence to standards and compliance. In the future, we’ll also see even more usage of these technologies.
Edge computing
Manufacturing generates vast amounts of data from IoT sensors, machines, and other devices. Edge computing enables processing this data at or near the devices and machines on the factory floor. This reduces bandwidth usage and lowers network latency. For manufacturing companies, it means instant data analysis and, as a result, faster decision-making without waiting for processing in the cloud. In general, the usage of edge computing in manufacturing increases the accuracy and speed of production management. In the future, this trend will only grow due to these benefits.
Summing up
AI is an indispensable tool for the industry 4.0 transformation amid ever-changing market demands. The technology offers new capabilities that help companies improve their process. As a result, manufacturing facilities can benefit from high-quality products, reduced downtime, resources optimization and increased efficiency of their organization.



Comments