Today, financial institutions and investors are increasingly seeking ways to maximize profits, improve risk management, and strengthen internal security. This is why they turn to artificial intelligence. It is a breakthrough technology that transforms how finance companies manage assets, internal operations, and customer experience as well.
As the financial businesses grow, client expectations rise, and technologies become more advanced, AI implementation becomes inevitable. Hence, the question arises, “Which financial AI solutions in finance are worth investing in to remain competitive tomorrow?”. In this article, we’ll discuss how to use AI in fintech, along with its core benefits, challenges, applications, and real-life examples.

The evolution of AI in fintech
At first, banks and financial institutions only gradually automated processes starting from the mid 20th century. The first card with a magnetic stripe developed by IBM occurred in 1969. Then, the most significant events were the emergence of the first ATM in 1967 and the rise of digital deposits and apps in the 2000s, such as Venmo and Zelle. These advancements changed the way people conduct financial transactions. Another important milestone was the creation of the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) in 1973. Its main goal was to create a secure, standardized system for exchanging financial messages globally.
Fintech has significantly expanded access to banking products and services, making them more convenient for clients. Furthermore, it has also streamlined many routine business processes. Today, financial companies offer a range of mobile apps and web-based services that enable banks to securely exchange customer data, automate a myriad of operations, and significantly improve customer experience. With so many financial solutions available, fintech startups focus on software development and partnerships with large banks, investment firms, and IT vendors. They aimed to integrate their solutions into the financial sector and facilitate how people manage their funds.
AI in fintech: future prospects
AI in fintech is growing fast and demonstrates incredible performance. Below, we’ve collected the most telling statistics that show the great potential of AI in the fintech market:
- According to Future Market Insights, the AI market in the financial technology sector will grow from $15.7 billion in 2025 to $68.5 billion by 2035, at a compound annual growth rate of 15.9%.
- Among all segments of the AI market in fintech, software will account for 67.7% of the total market value.
- The AI market in US fintech is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 15.7% between 2025 and 2035.
The main reasons for the growth of AI in the financial sector are digitalization, the need to process vast volumes of data, and a more personalized customer experience. The implementation of AI will enable financial institutions to optimize processes and make more effective real-time decisions.
What is AI in fintech?
Artificial intelligence in fintech refers to the the adoption of machine learning, natural language processing, predictive analytics, and other AI technologies to automate and enhance various financial operations and services. Machine learning models can analyze vast amounts of financial data, identify patterns, and make predictions or decisions without human intervention. Over time, these models learn from different types of data to improve their accuracy and reliability.
Mainly, artificial intelligence in fintech is used for:
- Fraud detection;
- Credit scoring and risk management;
- Trading and investment;
- Better customer service;
- Accounting and reporting;
- Regulatory compliance monitoring;
- Financial forecasting and planning.
8 use cases of AI in the financial industry
1. Fraud detection systems
AI-driven fraud detection systems analyze massive amounts of financial data, such as historical transactions and customer patterns, at speeds far beyond human capabilities. They can detect suspicious activity or anomalies in transactions, such as sudden large withdrawals or atypical spending patterns, and flag them for further investigation. Such systems are highly effective at adapting to new fraud techniques that people often remain uninformed about, helping them stay ahead of hackers. With the help of such systems, financial companies have reduced the number of false fraudulent claims by 60%.
It doesn’t mean AI fraud detection systems in banking and other financial facilities will replace traditional security systems. Instead, they will complement each other to achieve a higher level of system security.
2. Credit scoring and risk management
Traditional credit scoring methods rely heavily on the collection of historical financial data, such as credit history, income level, and existing debts. This process takes two to three weeks to complete and requires the involvement of many specialists. An AI-based credit scoring system is a mathematical model that uses statistical methods to analyze a broader range of data points, including social media activity, transaction patterns, total income, credit history, and more. It uses ML algorithms to build a more comprehensive and detailed profile of borrowers and assess the creditworthiness of loan applicants.
The system determines who qualifies for a loan based on customer, lender’s and market data. Then, it calculates a competitive interest rate based on risk scores and market trends. Credit scoring solution helps financial facilities reduce default rates by up to 25% and speed up the underwriting process.
3. Chatbots for customer service
The adoption of chatbots by banks and financial organizations is a strategic move to offer more initiative and hyper-personalized services. They provide round-the-clock customer support, addressing queries ranging from budgeting tips to fee reduction recommendations rapidly and accurately. Chatbots also assist customers in navigating a bank’s new offerings and services by providing personalized recommendations. They are able to successfully handle 80% of customer requests without the personal involvement of employees, thereby attracting new customers and reducing their churn rates.
Additionally, AI chatbots find applications in voice-based or computer vision face authentication. Users can seamlessly integrate them into home banking to validate transactions or access sensitive data. Virtual assistants powered by AI help finance companies build meaningful connections with clients and increase their engagement.

4. Robo-advisors
AI-powered online platforms, or robo-advisors, help individuals manage their investments and provide personalized financial services. Simply put, it is a virtual consultant that uses ML algorithms to make accurate predictions, create personalized investment strategies, and help you manage your finances more effectively.
First, the robo-advisor gathers information about a client, like financial goals, investment preferences, etc., through an online survey. Second, it automatically manages the portfolio by regularly buying and selling investments to keep it aligned with determined goals and market changes. Third, robo-advisors continuously monitor the portfolio and rebalance it to maintain the desired asset allocation. They offer services similar to those of human investment specialists, but are more accessible and cheaper for a wider range of investors. Thus, using robo-advisors makes it easy to open and manage investments over the long run.
5. Algorithmic trading
AI is rapidly advancing in high-frequency trading (HFT), a type of algorithmic trading that relies on execution speed to profit from small price fluctuations. ML algorithms analyze enormous amounts of financial data and execute real-time trades with incredible speed and accuracy. As a result, trading decisions are based only on analytical insights, mitigating the risks associated with human emotions.
ML algorithms are used to identify arbitrage opportunities, where minor differences in market prices can be exploited for profit. AI enables the development of complex models that predict market movements based on historical data and real-time market conditions. ML models are constantly trained and adapted to new data, which improves the accuracy of predictive models over time. AI also helps manage risk by analyzing market volatility and showing how it may impact trading decisions. This helps traders optimize their strategies and make smarter dealings.

6. Accounting and reporting
AI-enhanced solutions, particularly those powered by robotic process automation (RPA), significantly improve the efficiency and accuracy of financial tasks, such as:
- Document processing and data entry. AI-powered tools can process large volumes of documents much faster than humans, with near-zero errors, speeding up routine tasks.
- Profit and loss (P&L) statements. AI systems can automatically compile profit and loss statements by summarizing a company’s revenues and expenses.
- Accounts payable and receivable. AI systems can process invoices, send payment reminders, and validate financial data, speeding up transactions and minimizing errors.
Beyond that, AI-enhanced RPA solutions can understand the context and handle exceptions in reports. For example, if financial reports contain inconsistencies, AI systems can detect and address these anomalies. This ensures that the financial data remains accurate and reliable. As a result, AI сombined with RPA helps finance companies reduce internal transaction processing time by 80% and speed up document processing almost without errors.
7. Regulatory compliance
AI helps financial companies to stay compliant with national and international regulations, such as FATF Recommendations (AML/CFT), or anti-money laundering directive (AMLD). ML models can identify regulatory changes quickly, interpret their implications, and adjust compliance processes accordingly. This reduces the risk of non-compliance due to delays in understanding changing regulations. In addition, AI-powered systems can maintain detailed records and generate reports, providing an audit trail for compliance purposes and facilitating regulatory reporting.
AI enhances efficiency in compliance processes by automating tasks like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks. In KYC, machine learning models analyze customer profiles, behavior, and transaction history to assess risk levels and detect potentially suspicious activities. In AML, ML models monitor transactions in real-time to identify unusual patterns, anomalies, and potential money laundering activities. Thus, AI-based compliance greatly improves both the efficiency and effectiveness of regulatory risk management in financial institutions.
8. Financial planning and forecasting
AI enables personalized financial planning by leveraging advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms. ML processes and analyzes large amounts of data, such as individual income, spending patterns, and market trends. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, processes historical data and detects patterns to estimate potential risks, forecast market dynamics, and assess long-term financial performance. Based on these insights, AI generates tailored recommendations, such as customized investment strategies, savings plans, and budgeting advice. Banks using AI for financial forecasting have seen an average revenue increase of 12%. Thus, AI can help companies make better current and future financial decisions.
AI benefits in FinTech
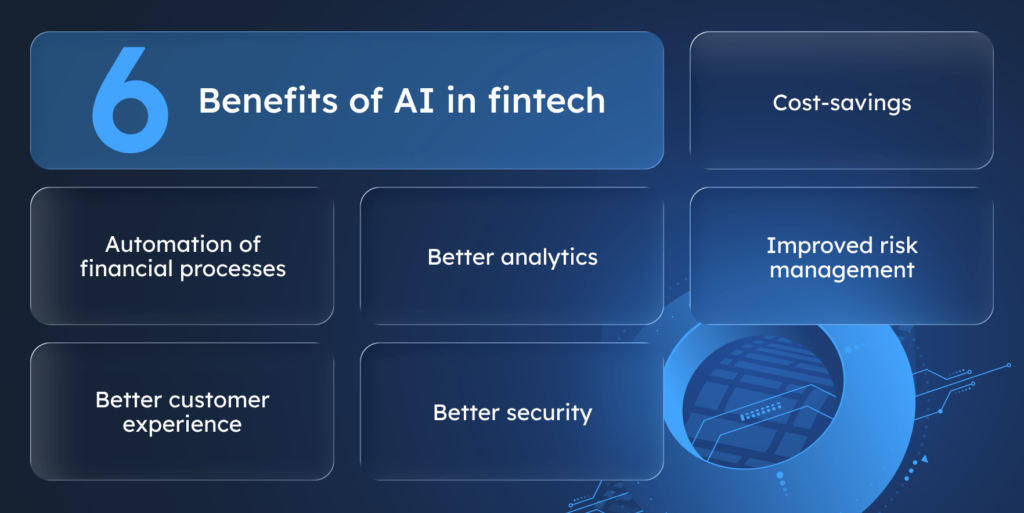
Financial companies of all sizes rely on AI solutions to optimize and accelerate their business processes. Here are what they’ve achieved:
- Automation of financial processes. AI automates traditionally manual financial tasks, like credit application analysis, invoice and payment processing, improving their efficiency, accuracy, and speed.
- Better customer experience. AI-powered solutions offer personalized customer support, quicker response times, and tailored financial products and recommendations.
- Better analytics. The use of well-trained ML models enables businesses to obtain deeper insights from their data, revealing hidden patterns and trends to make more informed financial decision-making.
- Better security. AI detects unusual patterns, anomalies, and security threats, ensuring that customer data and internal businesses’ systems remain protected.
- Cost savings. By automating financial processes and optimizing resource allocation, AI helps reduce operational costs and improve overall companies’ profitability.
- Improved risk management. AI analyzes large datasets in real time for risk assessment, enhancing decision-making and regulatory compliance for stable financial operations.
Main challenges of AI in fintech
Currently, there are many AI projects in the fintech sector that fail because companies encounter a number of serious problems that are best to be aware of in advance.
Data security and privacy
82% of organizations operating in the financial services sector reported data breaches in the past five years. This occurs because organizations and service providers manage sensitive customer information daily across multiple systems and integrations, which increases vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Solutions
- Implement effective security measures, such as end-to-end data encryption, multi-factor authentication, role-based user access based on a zero-trust approach, user activity monitoring, and regular risk assessments.
- Introduce data governance policies and procedures that define how data is processed and transferred within a company.
- Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix any vulnerabilities.
- Ensure that AI systems comply with relevant data protection laws, such as the GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
High implementation costs
The AI implementation requires significant investment in skilled specialists, hardware, software tools and scalable infrastructure that make it too expensive for most companies. These costs become even higher with the need for continuous AI maintenance and ML model retraining.
Solutions
- Start with small-scale projects to test the feasibility and effectiveness of an AI solution before committing to large-scale investments.
- Use advanced cloud-based services, such as AWS, Google Cloud to reduce on-premise hardware and infrastructure costs.
- Adopt open-source AI tools like PyTorch, TensorFlow, and LangChain and pre-trained models to reduce development and licensing costs.
- Consider partnering with AI development providers, like SoftTeco, to leverage expertise and resources at a lower cost than building in-house capabilities.
Poor data quality
The data may be incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate due to different data formats, missing values, errors or storage in siloed systems that are hard to integrate. This can lead to poor decision-making, reduced effectiveness of the ML models and, according to MIT Sloan research, a loss of 15-25% revenue.
Solutions
- Implement robust data cleaning and preprocessing techniques.
- Use real-time data quality checks to promptly identify and address issues.
- Utilize ETL pipelines and integration tools to consolidate and harmonize data from multiple systems.
- Build an organization-wide framework for managing and maintaining data quality.
ROI Uncertainty
One of the most significant risks of enterprise AI is the difficulty of demonstrating a clear return on investment, especially in the early stages. The benefits of AI can sometimes be indirect (e.g., improved decision-making) and may not be immediately apparent. This can make it challenging to gain stakeholder support and achieve the expected return on investment as fast as possible.
Solutions
- Start with a pilot project and establish clear, measurable KPIs.
- Engage AI consultants early on to determine which AI solutions best fit your budget, tech stack, and business objectives.
- Focus on the most profitable or efficient functions where AI can provide clear value.
Ethical and legal issues
AI models are trained on many diverse data sets that vary significantly in quality. So they can generate biases, untruths, or misleading information, resulting in unfair outcomes. Proper governance is one of the overlooked AI implementation challenges that can make or break its adoption.
Solution:
- Apply bias mitigation techniques during model development and ensure there are human-in-the-loop mechanisms in place.
- Implement clear governance policies that define how ML models are trained, evaluated, and monitored.
- Conduct regular bias audits and use diverse training datasets to prevent discrimination and ensure fairness across demographics.
- Continuously monitor ML systems for model drift, fairness metrics, and ethical compliance to ensure they operate safely.
Lack of skills and resources
Financial institutions and banks may lack the in-house experience and expertise to effectively implement and use AI. 70% of companies noted a shortage of qualified specialists, which makes the hiring process less straightforward than it may seem at first glance.
Solution:
- Use automated machine learning (AutoML) tools and frameworks that allow workers with limited AI expertise to build and deploy ML models.
- Invest in training and reskilling the in-house workers to help them master AI-based software, thereby facilitating user adoption.
- Hire short-term experts and consultants in relevant fields to complement your existing staff’s expertise.
AI implementation approach
For a successful AI implementation in fintech, several key areas require awareness and strategy. Firstly, ensure data quality and governance, as poor or biased data is the number one cause of failure for machine learning models. Closely tied to this, it is critical to address ethical and legal issues by conducting regular bias audits and implementing clear governance policies, including human oversight for key decisions.
Strategically, you must plan for the high implementation costs by starting with small, measurable pilot projects to demonstrate a clear and tangible return on investment (ROI) before scaling. Address the lack of specialized skills by investing in internal training and partnering with external experts to bridge the talent gap.
Finally, with sensitive financial data, prioritize a zero-trust security posture by mandating strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits to protect against cyber threats.
Real-life examples of artificial intelligence in fintech
Here are some real and quite successful examples of the integration of artificial intelligence in financial businesses.
Feedzai: a fraud detection platform
Feedzai introduced the RiskOps platform as a financial fraud detection solution that combines anti-fraud, AML monitoring, identity verification, and compliance. It uses AI technologies (machine learning, behavioral analytics, biometrics, device intelligence, etc.) to detect fraud, anomalies, and suspicious transactions in real time. Within months of implementing Feedzai, one payment service provider received 13 times fewer alerts and reduced fraud losses by $5 million. Furthermore, it greatly improved the customer experience.
Axyon AI: an investment platform
Axyon AI offers an investment management platform IRIS that utilizes advanced ML algorithms to improve investment decision-making. The system analyzes historical data, and market trends to provide predictive insights into asset performance, risks, and potential opportunities. It suggests optimal asset allocations based on risk tolerance, return objectives, and market conditions. Axyon AI partners with industry giants like Microsoft, IBM, and Nvidia and provides its services to commodity traders and asset managers.
Kasisto: a conversation AI platform
Kasisto introduced the famous conversational AI solution designed for the banking industry called KAI. With natural language processing and advanced ML algorithms, it delivers intuitive and around-the-clock customer support, helping customers make informed financial decisions. It enables customers to manage their accounts, understand their transactions, explore loan or credit options, and receive instant, personalized insights. As a result, the platform enables banks to reduce contact center workload while simultaneously achieving outstanding customer service.
Upstart: a credit scoring platform
Upstart is an AI-powered credit scoring and lending platform that partners with over 100 banks and credit unions to predict consumer creditworthiness. It uses predictive modeling and ML algorithms to analyze thousands of factors, such as income stability, education, and existing credit behavior. Based on them, it predicts the risk of default or early repayment for each loan. By leveraging AI, the system improves credit decision accuracy, allowing banks to increase approvals while reducing the risk of non-payment.
Conclusion
AI brings a wide range of solutions to the financial industry and is already delivering a competitive advantage to early adopters. Despite the potential risks associated with AI, with careful planning and a well-developed implementation strategy, companies can improve internal processes, increase decision-making accuracy, and provide more personalized customer service. To make the AI implementation process easier, it’s recommended to consult with an experienced AI development provider like SoftTeco, who offer comprehensive ML development services. Our specialists will define the best AI strategy and select the most effective tools and technologies to help you achieve your business goals faster.



Comments