Today’s consumers are increasingly leaning toward online shopping. According to Oberlo, the number of digital buyers reached 2.71 billion in 2024. This highlights the growing importance for ecommerce businesses to deliver a frictionless and secure payment process. With this in mind, selecting the right payment gateway becomes crucial, as it directly impacts both customer experience and conversion rates.
However, picking the right payment gateway can be tricky. To succeed in it, you’ll need to carefully evaluate various factors, like security, transaction fees, supported payment methods, etc. Below, we’ll cover everything about ecommerce payment gateways, including how they work, main types, and tips for smooth choosing and integration, with notable examples.
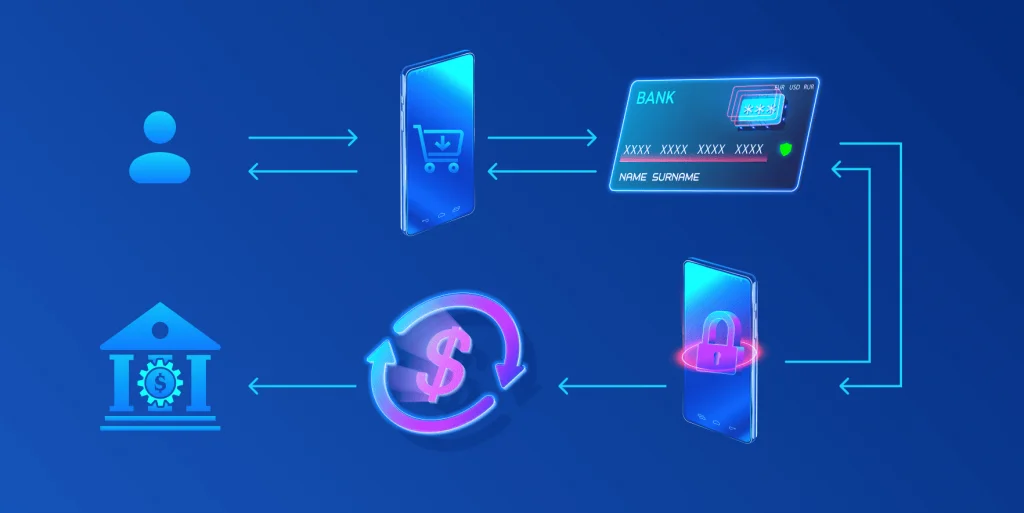
What is a payment gateway in ecommerce?
What is a payment gateway in ecommerce? Simply put, it’s a service that handles online payments. It acts as a bridge, transferring payment details from the customer to the bank and then sending back payment confirmation. It ensures that sensitive data, like credit card details, is encrypted and protected. By enabling businesses to accept various payment methods across websites, mobile apps, and physical stores, payment gateways ensure smooth, secure, and efficient transactions.
Key functions of a payment gateway in ecommerce are:
- Processing payments
- Authorizing transactions
- Confirming payments
- Managing multiple payment options
- Converting currencies
- Preventing fraud
In short, payment gateways ensure security, smooth checkout, and easy payment management – all necessary to create a successful online store.
How do payment gateways work?
Here’s how a payment gateway typically works:
- Customers make a purchase: the customer picks items and goes to checkout, where they choose a payment method;
- Encryption: the payment gateway encrypts the collected data from the customer’s browser to keep it secure while being sent;
- Authorization request: the encrypted data is sent to the payment processor, which forwards it to the customer’s bank for authorization;
- Processing: the payment processor sends the transaction to the card network (like Visa or Mastercard), which then sends it to the customer’s bank to get approval for the payment;
- Bank response: the bank checks the transaction details (like available funds and fraud checks) and sends an approval or decline response to the payment gateway;
- Confirmation: the payment gateway informs the merchant whether the payment was approved or declined;
- Transaction completion: if approved, the payment gateway settles the payment, transferring the funds to the merchant’s bank account.
This process happens within a few seconds and ensures secure and efficient transactions in online shopping. Now let’s look at the different types of payment gateways usually used in ecommerce.
Main types of payment gateways
All payment gateways have one mission – to process online transactions. However, they differ in how they integrate with websites and how they handle payments. Here are the four main types:
- Hosted payment gateways
This type of gateway is hosted by a third-party service provider. Customers are redirected to a third-party payment page to complete their purchase. This gateway is easy to set up but offers less control over the checkout experience.
Examples: PayPal and Amazon Pay.
- Self-hosted payment gateways
Customers enter their payment details on the merchant’s website, but the payment is processed by an external provider. Companies have full control over the entire checkout process and customer experience. As businesses process payments on their own websites, they must comply with data protection standards, including the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Examples: Shopify, and Authorize.Net.
- API payment gateways
Businesses integrate payment processing directly into their website or app using an API. It offers more control over the user experience and customization options but requires technical expertise. Since payment data is processed on the merchant’s side, businesses also must adhere to PCI DSS and other security standards.
Examples: Stripe and Braintree.
- Local payment gateways
These gateways directly integrate with local banks to process payments. This type is often used in a specific region or country, as local banks are usually trusted and familiar. It redirects customers to their bank’s payment platform to complete the payment. Its efficiency depends on the bank’s technology and support for online transactions.
Examples: Klarna in Europe, and Rede in Brazil.
Each payment gateway type has its advantages and is suited for different business needs. So, let’s consider the core differences between them in depth.
Differences between payment gateway types
In the table below, we list the main differences between various types of ecommerce gateways:
| Hosted | Self-hosted | API | Local | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integration | Easy to integrate | Highly complex and requires tech expertise | Complex and requires tech expertise | Depends on a provider |
| Pricing and transaction fees | High fees with no initial setup fee | Low fees, but high initial setup | Transaction fees vary, but low setup fee | High transaction fees, but initial setup vary |
| Technical complexity | Low | Medium | High | Medium |
| Security | High (handled by a gateway) | Moderate (handled by a merchant) | High (gateway provides tools, but merchant must implement them securely | Moderate\ High (depends on local bank) |
| Customization | Limited | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Custom experience | Redirected to the gateway | Stays on the merchant site | Stays on the merchant site | Depends on the integration |
| Best for | Small and SMB businesses | Large and medium businesses | Large and medium businesses | Local businesses |
Now that we’ve considered the key differences between payment gateway types, let’s look at the best options available and explore them.
6 best ecommerce payment gateways in 2025
Here are the best payment gateways for ecommerce in 2025 and beyond, along with their pros, cons, and pricing.
PayPal
PayPal is one of the widely used payment platforms. It operates in 203 countries, with around 435 million accounts, and processes over $22 billion in transactions. It is suitable for businesses of all sizes and supports different payment options, including credit/debit cards (Visa, American Express), PayPal balances, and linked bank accounts. In some areas, it supports buy-now-pay-later services.
Established in 1998, PayPal has become a top choice among businesses and consumers due to its simplicity and customization options. Over the years, PayPal has expanded its offerings, including partnerships with major retailers (Walmart, eBay), and offers the ability to buy, hold, and sell cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Pricing: PayPal follows a tiered pricing structure, which varies based on the location and type of transaction. The standard fee is typically 2.9% + $0.30 for domestic transactions, but international fees can go up to 4.4% + fixed fees depending on the country.
Pros
Cons
Stripe
Stripe is another leading payment gateway platform that enables businesses to accept online payments seamlessly. It operates in over 30 countries across Europe, Asia, and America. Also, it integrates with numerous ecommerce platforms, accounting software, invoicing tools, etc, providing a seamless user experience. In 2023, Stripe processed over $1 trillion in payment volume, demonstrating its global reach.
Stripe allows businesses to accept various payment methods (credit\ debit cards, digital wallets) and supports over 135 currencies. Also, it provides features to help businesses handle recurring payments, such as subscriptions and automated invoicing. This is useful for companies that charge customers regularly (e.g., monthly or yearly subscriptions).
Also, it offers tools for managing recurring billing, subscriptions, and invoicing, suitable for subscription-based businesses.
Pricing: Stripe uses a pay-as-you-go pricing model with flat-rate transaction fees for most of its services. Its transaction fees are 2.9% + $0.30 per successful card transaction for domestic cards in the U.S. Its additional charges include 1.5% for international cards, 1% for currency conversion, and 0.5% for manually inputted cards.
There are no setup or monthly fees. Additional services like Stripe Radar (fraud prevention) or Stripe Connect (for marketplaces) may come at extra costs.
Pros
Cons
Square
Square is a complete payment processing platform for both online and in-person payments. For online payments, Square provides APIs and e-commerce tools that allow businesses to accept payments on their websites and mobile apps. For physical shops, Square offers hardware such as card readers and terminals that allow you to accept payments in person.
This platform is particularly popular among SMBs due to its easy setup and transparent pricing. Moreover, it is also known for its user-friendly system, making it a go-to solution for companies with limited technical expertise.
Pricing: Square uses a flat-rate pricing model, which is simple and transparent. It charges 2.6% + $0.10\transaction for in-person payments, 2.9% + $0.30\ transaction for online payments, 3.5% + $0.15\transaction for manually payments (via Virtual Terminal) and 3.3% + $0.30\transaction for invoices paid online.
Pros
Cons
Amazon Pay
Amazon Pay is the most prominent digital payment service owned by Amazon. It operates in 18 countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, etc., and has processed 2.5 billion transactions globally. The platform allows customers to make purchases on external websites and apps using their Amazon account credentials. This speeds up checkout and eliminates manual entry.
Amazon Pay provides robust security measures and supports mobile payments and different payment methods, like credit\debit cards, bank transfers, and Amazon Pay balance. It offers features, like recurring payments, one-click checkout, and voice transactions via Alexa. Also, it supports international payments with multi-currency support, helping businesses expand their presence.
Pricing: Amazon Pay charges fees on a per-transaction basis. It does not charge setup fees, monthly fees, annual fees, or termination fees. The standard fee for web and mobile transactions in the US is 2.9% + $0.30\transaction. There is also a fixed fee per transaction based on the currency used.
Pros
Cons
Authorize.net
Being one of the oldest payment gateways, Authorize.net operates in over 33 countries and supports over 400,000 customers globally. It is owned and operated by Visa, the card network. One key benefit is the ability to accept credit card and electronic check payments through a website and over an Internet Protocol (IP) connection. It provides a secure way to process transactions (online, in-person, and manual) and offers features like fraud prevention, recurring billing, and customer information management.
Moreover, Authorize.net is easy to set up and use, reliable, and allows multiple integrations with other solutions. It focuses on reducing chargebacks through advanced fraud-detection algorithms to protect your business and customers.
Pricing: it consists of a combination of setup, monthly, and transaction fees. It offers three pricing plans: All-in-One Option, Payment Gateway, and Payment Gateway & eCheck. They include a setup fee of $0.00, a monthly gateway fee of $25.00, a per-transaction fee of $0.30 + 2.9% or $0.10 (for the two last plans), and an additional daily batch fee of $0.10.
Pros
Cons
Shopify Payments
Shopify Payments is a native payment gateway that allows merchants to accept online payments directly through their Shopify store. This makes it easy to set up and manage payments without the need for third-party integrations. Also, it provides all the needed features for payment processing, order management, and analytics in one place, so you can easily track sales and manage your finances.
Shopify Payments offers lower transaction fees and supports multiple payment methods, such as credit cards (Visa, Mastercard), digital wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay), and buy now, pay later options via partners like Klarna. It also supports multiple currencies, allowing companies to sell in different currencies and reach a global audience.
Pricing: Shopify Payments has a transparent pricing structure that varies based on your chosen Shopify plan. You can consider the Basic plan for $39/month, Shopify for $105/month, Advanced for $384/month, and Shopify Plus (Enterprise plan) for $2,300/month. Payment processing fees start at 0.6% (varies by plan and region), and currency conversion fees are 1.5% (US) and 2% (for other countries and regions).
Pros
Cons
The main differences between the best ecommerce payment gateways
Here’s a brief comparison for each payment gateway that we’ve talked above:
| PayPal | Stripe | Square | Amazon Pay | Authorize.net | Shopify Payments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setup process | Easy and quick | Requires coding | Simple | Simple for Amazon sellers | More complex | Easy and quick |
| Pricing | 2.9% + $0.30\transaction | 2.9% + $0.30\transaction | 2.6% + $0.10\transaction and $2.9%+$0.30 online | 2.9% + $0.30\transaction | 2.9% + $0.30 + 25\month fee | Varies and based on Shopify plan |
| Currencies | 25+ | 135+ | 5 | 12 | 7 | 135+ |
| International support | 200+ countries | 46+ countries | Available in the US, Canada, Japan, Australia, and the UK | 20+ countries | Available in the US, Canada, UK, Europe, and Australia | 175 countires |
| Payout speed | 1-2 business days | 2 business days | Next business day | 3-5 business days | 2-3 business days | 1-3 business days |
| Recurring billing | Yes | Yes | Yes | Limited | Yes | Yes |
| Mobile payment | Yes | Yes | Yes (primary focus) | Limited | Yes | Yes |
| Fraud protection | Advanced | Advanced in-built fraud prevention tools | Basic | Amazon’s fraud detection | Advanced Fraud Detection Suite (AFDS) | Basic |
| Customization | Limited | High | Limited | Limited | Moderate | Limited |
| Best for | Small and medium businesses | Small and enterprise businesses | Small businesses, in-person and online sales | Amazon customers | Established businesses with high-volume transactions | Shopify store owners |
After looking at the best payment gateways around the globe, the next step is choosing the right one for your business.
How to choose the right ecommerce payment gateway
As we said above, choosing the right payment gateway for your online store can be a challenging task. To ensure a smooth and secure transaction process for both you and your customers, you’ll need to evaluate key factors, like:
Business model and volume
To determine the right payment gateway, you need to consider your business size, transaction volume, and specific needs. For example:
- For small businesses, if you just started your business or handle a low volume of transactions on a regular basis, it is best to use a hosted gateway. You can set up and maintain it easily, thus being able to focus on growing your business without worrying about complex infrastructure.
- For growing businesses: as your transactions increase in volume, you may consider an API-hosted gateway. It provides more flexibility and improved customer experience and can help reduce costs compared to a hosted solution.
- For large businesses: if you have high transaction volumes and need customized payment solutions, choose a self-hosted gateway. It gives you full control and flexibility to meet your specific needs. But, it comes with responsibility for security, maintenance, and infrastructure.
In a nutshell, you need to select an ecommerce gateway solution that aligns with your current and future business goals.
Security standards
Security is a top priority for all ecommerce companies. When choosing a payment gateway, it’s important to ensure it meets the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This is a widely accepted set of rules and procedures designed to secure credit, debit, and cash card transactions. Its main goal is to reduce the risk of fraud for organizations and prevent cybersecurity breaches.
While PCI DSS is not a law, most businesses that deal with credit card transactions must follow it to maintain a secure environment for customers. Among other security standards to follow are:
- Data Encryption: payment gateways use SSL/TLS encryption to secure payment data between a user’s browser and the server.
- 3D Secure Authentication: this adds extra layers of security by requiring customers to verify their identity through their bank during online transactions.
- Tokenization: the process replaces sensitive card information with a unique identifier (token) that cannot be exploited if intercepted;
- Fraud Detection Tools: features like Address Verification System (AVS), CVV checks, and fraud analytics help detect and prevent fraud.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): this adds additional layer of user verification, such as using one-time passwords (OTPs) or biometric verification.
Some payment gateways also offer built-in fraud detection. Be sure to choose a gateway that offers robust security features and keeps customer data protected.
Transaction fees
Transaction fees are another key factor to consider when comparing different payment gateways. These fees are charged for each transaction made through the gateway. They can vary based on factors, such as the payment method, the volume of transactions, and the service provider. Examples of such fees:
- Monthly fees
- Setup fees
- Transaction fees
- Chargeback fees
- Refund fees
- Cross-border fee
Also, watch out for hidden costs, like the Merchant Discount Rate (MDR). It is a fee payment processor charge for each sale. For example, if you sell an item for $100 and the MDR is 2%, the processor takes $2, and you receive $98. This fee is usually part of the total payment processing cost and other charges listed above. MDR is important to consider when choosing a payment gateway as it can add up, especially for businesses with many transactions.
Thus, businesses should carefully consider fees to find a payment gateway that suits their transaction volume. Keep in mind that the lowest fee isn’t always the best choice, as it can come with compromised service or limited features.
Support for multiple payment methods
Not all gateways support every payment method. Hence, you need to choose a payment gateway that supports the payment methods preferred by your target customers. This could include credit\debit cards, digital wallets, buy-now-pay-later options, or even alternatives, like cryptocurrency. A modern payment gateway must accommodate different payment preferences.
For businesses, it will help expand the customer base and improve conversion rates. For customers, it will reduce friction at checkout and make the shopping experience more convenient.
Seamless integration
A payment gateway should easily integrate with your website or an app. If the gateway doesn’t integrate well, it can cause errors, slowdowns, or disruptions in the service. As a result, it leads to a negative user experience and, in turn, lost sales as frustrated customers abandon their carts. To avoid these issues, choose the gateway that offers either well-documentation APIs, SDKs, or plugins for popular ecommerce platforms. This ensures smooth online payment gateway integration.
Also, if you plan to scale your business, opt for a gateway that provides flexible integration options capable of growing with your needs.
Customer experience at checkout
A complicated checkout process is a common reason why 28% of customers abandon their shopping carts. Hence, a confusing checkout with unnecessary steps can lead to a bad customer experience, reduced conversion rates, and lost revenue. To avoid negative fallout, you should select a payment gateway partner that offers a quick and simple interface with minimal steps to complete transactions.
To help you with it, we’ve put together a list of features that you should look for in your payment gateway:
- One-click payments
- Recurring billing for existing customers
- Multi-currency support
- Customizable checkout pages
- Support for multiple payment options
- Fast processing speed
- Mobile optimization
Custom support
Most businesses handle large amounts of money through their payment gateway daily. If the gateway crashes, it can lead to significant financial losses and poor customer experience. To avoid this, choose a payment provider with reliable customer support. This wil help keep operations running smoothly during potential technical issues or integration challenges. A payment provider’s support should include:
- 24/7 availability
- Multiple contact options (live chat, phone, email)
- Clear, detailed documentation
- A dedicated account manager
- A helpful support team
Analytics and dashboards
To effectively manage customer payments and business performance, you need clear reporting and analytics. So, look for a payment gateway that provides real-time insights into sales, customer data, and transactions on your website. Focus on features like transaction reports, revenue tracking, and customizable dashboards to optimize your business strategies.
These tools can help you monitor cash flow, identify trends, and make the right decisions to improve customer experience and profitability. Moreover, choosing a payment gateway with integrated analytics will save time by consolidating the data in one place, thus reducing the need for manual reporting.
Steps to integrate a payment gateway into your ecommerce store
Integrating a payment gateway into your website might seem tricky, but it can be a smooth and simple process with the right approach. Here’s a step-by-step payment gateway integration process:
Step 1: Choose the right payment gateway
Previously, we’ve discussed the key aspects of choosing the right payment gateway for your online store. In a nutshell, you’ll need to analyze factors like transaction fees, custom support, payment methods, user experience, security, global reach, and more. Each of these elements contributes to your store’s efficient and secure operation.
Step 2: Set up a merchant account (if needed)
Set up a merchant account with your chosen payment service provider. A merchant account is a special business bank account that allows you to receive online payments. In some cases, you won’t have to set it up. Some payment gateways, like Stripe, combine merchant account functionality and payment gateway for easy setup.
After that, you need to verify your identity before you can start accepting payments. This often includes providing additional documentation (e.g., passport, business registration).
Step 3: Obtain API credentials
Once you’ve set up your payment gateway account, you must obtain API keys. These keys are unique identifiers that connect your website or app to the payment gateway. They ensure secure communication between your platform and the gateway’s servers. Depending on your payment gateway provider, you may have to generate or retrieve API credentials.
To set up API credentials, you need to log in to your account and navigate to the API or developer section. In this section, you’ll find options for generating API keys and other authentication credentials. You must follow the instructions provided by the payment gateway to develop the necessary credentials.
Step 4. Choose the integration method
This step involves deciding how to link the payment gateway to your website. The method that you choose will depend on your technical capabilities, the options provided by the payment gateway, and how well it works with your platform. Here are three common integration methods:
- Hosted payment pages: the payment gateway handles the entire transaction process on a separate page, reducing the need for technical implementation on your site. It’s easy to set up but may offer less customization.
- Direct API integration: you integrate the payment gateway directly into your site or app, giving you full control over the user experience and payment flow. It requires more technical expertise but offers more flexibility.
- Platform plugins\extensions: most ecommerce platforms (like Shopify Magento) offer pre-built plugins\extensions for easy integration. This method simplifies setup but may have limitations in terms of customization.
Step 5. Integrate the payment gateway
Once you’ve chosen your integration method, you must follow the payment gateway’s guide to connect it to your website.
- For hosted payment pages: follow the instructions to generate payment links or buttons. You’ll usually get code snippets or HTML elements to add to your checkout page.
- For direct API integration: you’ll need to use languages like PHP or JavaScript to connect to the payment gateway’s API. The payment provider’s documentation will give you code examples and details on handling API endpoints and responses.
- For platform plugins/extensions: you’ll need to install the plugin\extension from your ecommerce platform’s marketplace. Then, configure the plugin settings with your API credentials and other required information.
Step 6. Configure payment settings
Once the gateway is integrated, you’ll need to customize the payment settings to fit your business needs. To do this, go to the settings section of your ecommerce platform or website admin panel. In the payment settings, you’ll be able to:
- Set supported currencies
- Choose payment methods
- Enable security features
- Set shipping options
Ensure the payment settings align with your business needs and comply with any legal or industry requirements.
Step 7: Test the integration
To prepare for going live, you’ll need to test the payment gateway integration. Most payment gateway providers offer a “sandbox” or a testing environment that allows you to simulate transactions and check that everything is working correctly. During testing, verify that:
- Payments are processed correctly
- Test different payment scenarios with the gateway
- Errors are handled smoothly with proper user notifications
- Security measures, such as encryption and tokenization, are functioning
Testing should cover multiple devices, browsers, and payment methods to ensure compatibility and reliability. Once testing is complete, fix any issues and retest before moving to production.
Step 8. Go live and monitor transactions
Once everything is tested, you can switch to live mode. After going live, you must monitor your payment gateway’s performance and transactions to spot any issues quickly. Also, update your payment gateway with the latest security features. Use the payment gateway’s reporting tools to analyze data and ensure smooth payment operations.
Ecommerce payment gateway trends for 2025
As technology continues to evolve, so too will consumer expectations and behaviors. Here’s what the future potentially holds for ecommerce payment solutions:
Contactless payments
The trend toward contactless payments has gained significant popularity, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Сonsumers prefer fast and more convenient ways to pay and do it via technologies like Near Field Communication (NFC) and mobile wallets. By touching your card or smartphone to the terminal, consumers can make a payment. This is usually used for purchases in shops, cafes, and other points of sale.
Contactless payments help buyers avoid physical contact during transactions, enhance their experience, and streamline operations.
Digital wallets
Modern customers value speed during checkout and prefer simple transactions. Digital wallets, like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal, meet this demand. According to Forbes, 53% of shoppers use these digital wallets more often than traditional payment methods. Users can make quick purchases without entering card details each time, saving them time and effort. This approach improves the shopping experience, reduces cart abandonment, and drives sales.
Artificial Intelligence
As customers expect fast, safe, and more personalized services, AI integration in payment gateways becomes more vital. With the help of AI and machine learning, companies can detect and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time. Also, they can analyze transaction pattern, customer behavior to identify potential risks and anomalies. This is especially important in today’s tech world in which cyber threats are constantly evolving.
Also, AI helps automate customer support via chatbots and virtual assistance. They make it easier for users to resolve payment issues without human intervention. Overall, the ability of AI to predict and adapt to user preferences makes payment experiences more personalized.
Multi-currency support
As ecommerce grows, companies are increasingly looking to expand into global markets. The main thing that can help them do this is multi-currency support. In other words, customers can shop in their own currency, which makes their shopping easier and more affordable.
In order to adapt to this trend, payment gateways are offering automatic currency conversions, real-time exchange rate updates. This helps companies avoid the necessity of having to manage multiple payment systems for different countries. Thus, multi-currency support reduces barriers for international customers and streamlines cross-border transactions.
Buy now, pay later (BNPL) options
Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) allows shoppers to split payment into smaller installments, usually over weeks or months. There’s usually no interest if paid on time, but late payments may result in fees or interest charges. This payment method can encourage more purchases, especially for those who might hesitate otherwise.
According to McKinsey, 30% of users use BNPL, and 29% say they would have bought less without it. While it may not be right for every business, it’s becoming popular as it appeals to customers seeking flexibility in payments. However, companies should carefully consider their target audience and the financial impact before implementing it.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency provides businesses and customers with a secure, fast, and decentralized way to make transactions. With cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc., some ecommerce platforms are integrating crypto payments to cater to the needs of tech-savvy users. Its key benefits include low fees, fast processing, better security via blockchain, and cross-border transactions without intermediaries.
Big companies like Microsoft, Tesla, and Expedia have started accepting cryptocurrencies to attract more customers. However, the lack of central regulation makes both governments and businesses cautious about fully adopting it. Despite this, cryptocurrency is growing in ecommerce, driven by its speed, cost, and security.
Biometrics
Biometric authentication is becoming a popular trend in ecommerce for payment verification. Instead of using passwords or PINs, consumers can now use secure and easy options like fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice identification. This makes it harder for fraudsters to replicate or tamper with, giving consumers peace of mind.
These trends reflect a push toward seamless, secure, and convenient payment experiences that meet needs of tech-savvy users globally.
Conclusion
Selection and implementation of the right ecommerce payment gateway are crucial for the success and growth of your online store. Understanding the various types of payment gateways, their ins and outs, current trends, and tips for smooth integration and setup – listed in this article- helps you better understand what is best for you. By carefully comparing options and conducting thorough research, you can make sure smooth, secure, and convenient transactions for modern users.
If you need a professional consult, turn to SoftTeco’s ecommerce services that help you effectively integrate and optimize ecommerce payment gateways.


Comments